GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Product rule for counting How to calculate probabilityThis topic is relevant for:

Systematic Listing Strategies
Here we will learn about systematic listing strategies, including calculating probabilities.
There are also counting strategies worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are systematic listing strategies?
Systematic listing strategies are ways of writing outcomes from an event in an organised way with none of the possibilities missed out or repeated. Writing all possible items in a set is known as enumeration.
To do this we need to use a method which makes listing items easier. A good method to use is to fix certain values, making only small changes between each item in the list.
For example,
A meal deal consists of a drink and a bag of crisps.
The drinks available are orange juice or apple juice.
The crisp flavours are bacon, cheese or plain.
To start listing all the possible combinations, we can begin by shortening the names of each flavour of drink and crisps.
Drinks – \text{O} and \text{A}
Crisps – \text{B, C} and \text{P}
Start by fixing the choice of drink to \text{O} and then change the crisp flavour.
\begin{aligned} &\text{O, \ B} \\ &\text{O, \ C} \\ &\text{O, \ P} \end{aligned}Now change the drink flavour and repeat the crisp flavours in the same order as before.
\begin{aligned} &\text{A, \ B} \\ &\text{A, \ C} \\ &\text{A, \ P} \end{aligned}This gives us 6 combinations in total.
This can be checked using the product rule for counting.
The were 2 flavours of drink and 3 flavours of crisps, so the total number of possible outcomes is 2 \times 3=6.
Step-by-step guide: Product rule for counting
What are systematic listing strategies?

Listing outcomes and related probabilities
Once we have listed the possible combinations, these outcomes can be used to calculate the probability of events occurring.
For example,
A 3 sided spinner labelled 2, 4, 7 is spun and a double sided counter labelled 5 and 8 is flipped.
List the possible combinations that could be obtained and find the probability that the sum of the combination is 12.
Using systematic listing, we can see that the possible combinations are,
2,5 \ (sum to 7)
2,8 \ (sum to 10)
4,5 \ (sum to 9)
4,8 \ (sum to 12)
7,5 \ (sum to 12)
7,8 \ (sum to 15)
There are 6 possible combinations and two of them sum to 12.
Therefore, the probability of obtaining a sum of 12 is \frac{2}{6}=\frac{1}{3}.
How to use systematic listing strategies
In order to use systematic listing strategies:
- Use a single letter or number for each item to be selected.
- Determine the number of items to be selected.
- Fix a first choice item. Follow a pattern for selecting second, third choices etc, fixing those where appropriate to ensure no options missed or unnecessarily duplicated. Repeat with a new first choice item.
Explain how to use systematic listing strategies


Probability of events worksheet (includes systematic listing strategies)

Get your free systematic listing strategies worksheet of 20+ probability of events questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Probability of events worksheet (includes systematic listing strategies)

Get your free systematic listing strategies worksheet of 20+ probability of events questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on combined events
Systematic listing strategies is part of our series of lessons to support revision on combined events. You may find it helpful to start with the main combined events lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Systematic listing examples
Example 1: listing outcomes selecting from two sets
A coin is flipped and a spinner numbered 1, 2, 3 and 4 is spun.
Write a list of the possible outcomes.
- Use a single letter or number for each item to be selected.
Use \text{H} and \text{T} for the sides of the coin and numbers 1,2,3,4 for the spinner.
2Determine the number of items to be selected.
One item from each is to be selected.
3Fix a first choice item. Follow a pattern for selecting second, third choices etc, fixing those where appropriate to ensure no options missed or unnecessarily duplicated. Repeat with a new first choice item.
Start by fixing the coin and change the spinner number.
H1, H2, H3, H4Now change the side of the coin and repeat the order of the spinner.
T1, T2, T3, T4There are 8 outcomes in total.
Example 2: listing outcomes selecting from three sets
A meal offer at a restaurant gives you a choice of main, side and drink.
| Main | Side | Drink |
|---|---|---|
| Burger | Garlic Bread | Juice |
| Fish and Chips | Salad | Lemonade |
| Pasta | Cola |
List the possible combinations of main, side and drink.
Use a single letter or number for each item to be selected.
Use B, F and P for the mains.
Use G and S for the sides.
Use J, L and C for the drinks.
Determine the number of items to be selected.
One item from each is to be selected.
Fix a first choice item. Follow a pattern for selecting second, third choices etc, fixing those where appropriate to ensure no options missed or unnecessarily duplicated. Repeat with a new first choice item.
Start by fixing the main, then the side and change the Drink, then change the side and repeat the pattern of the drinks.
\begin{aligned} &BGJ, BGL, BGC \\ &BSJ, BSL, BSC \end{aligned}
Now change the main, repeating the process for the sides and drinks:
\begin{aligned}
&FGJ, FGL, FGC \\
&FSJ, FSL, FSC
\end{aligned}
\begin{aligned}
&PGJ, PGL, PGC \\
&PSJ, PSL, PSC
\end{aligned}
There are 18 outcomes in total.
Example 3: listing outcomes to give a set total
A car park charges 80p for a day of parking. The ticket machine only accepts 50p, \ 20p and 10p coins. List all the possible combinations of 50p, \ 20p and 10p coins to make a total of 80p. The order of the coins does not matter.
Use a single letter or number for each item to be selected.
Use 50, \ 20 and 10.
Determine the number of items to be selected.
There will be different amounts of each but the sum of each combination must be 80.
As the order of the coins does not matter, 50, 20, 10 is the same as 50,10, 20.
Fix a first choice item. Follow a pattern for selecting second, third choices etc, fixing those where appropriate to ensure no options missed or unnecessarily duplicated. Repeat with a new first choice item.
Start with using a 50p coin, introduce a 20p and then without a 20p.
\begin{aligned} &50, 20, 10 \\ &50, 10,10,10 \end{aligned}
Now list combinations without a 50p coin, but using 20p coins, reducing the number of 20p coins each time.
\begin{aligned} &20,20,20,20 \\ &20,20,20,10,10 \\ &20,20,10,10,10,10 \\ &20,10,10,10,10,10,10 \end{aligned}
Last combination is just 10p coins
10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10
There are 7 combinations in total.
Example 4: listing outcomes to find a number of items from a diagram.
The diagram shows a shape made from five points A, B, C, D and E. \ BCDE is a straight line.
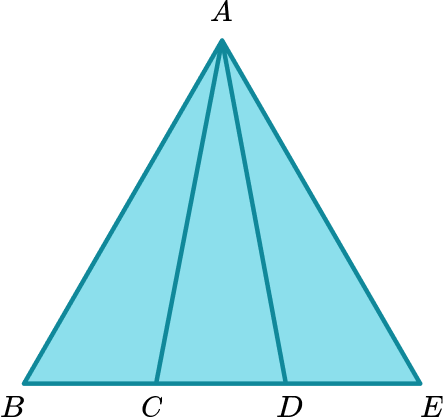
Find the number of triangles in the diagram.
Use a single letter or number for each item to be selected.
To list the triangles we will use three of the letters A,B,C,D and E.
Determine the number of items to be selected.
Each triangle must include the point A as the others are on a straight line. So the combinations will be A and two other letters.
The order of the letter does not matter, so triangle ABC is the same triangle as ACB.
Fix a first choice item. Follow a pattern for selecting second, third choices etc, fixing those where appropriate to ensure no options missed or unnecessarily duplicated. Repeat with a new first choice item.
Start by fixing A and B and change the third letter.
ABC, ABD, ABE
Now change second letter in the combination and repeat the process
ACD,ACE \ ( notice that we do not write ACB since this is the same as ABC) \ ADE .
There are 6 triangles in total.
Common misconceptions
- Lists are created randomly with no pattern
Common errors are made when students forget to follow a pattern or do not “fix” items in their combinations. It is important to use a systematic approach to ensure all combinations are listed. Small changes for each combination help with this.
- Students do not consider if order matters
When listing outcomes it is important to think about the order of the combinations and whether it matters. For example, if flipping two coins, does the situation need HT to be different to TH.
Practice systematic listing strategies questions
1. A three sided spinner labelled A,B,C and a coin labelled H and T are used to create outcomes. The spinner is spun and the coin flipped. What is the correct list of possible outcomes?




Select one letter from each of the spinner and coin and make pairs.
2. In year 9, students at a school can choose a humanities option, a language option and a creative option.
| Humanities | Language | Creative |
| Geography (G) History (H) RS (R) |
French (F) Spanish (S) |
Art (A) Drama (D) |
Which of the following is not a valid combination?




H and R are both humanities options so cannot both be selected.
3. In year 9, students at a school can choose a humanities option, a language option and a creative option.
| Humanities | Language | Creative |
| Geography (G) History (H) RS (R) |
French (F) Spanish (S) |
Art (A) Drama (D) |
What would be a sensible first two combinations to list?




Fix G and F as they are the first in each category and then change the creative option.
4. A square grid is 4 squares by 3 squares. Each vertex is labelled with a letter.
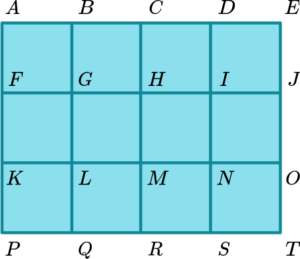
Using a systematic approach, find the total number of squares in the grid.




There are 12 small squares, 6 which are 2 by 2 and 2 which are 3 by 3.
5. A football team plays 3 games. They get 3 points for a win, 1 point for a draw and 0 points for a loss.
How many different results could give the football team 5 points or more from the three games?




The possible ways of getting 5 or more points are 3 wins, 2 wins and a draw, 2 wins and a loss or a win and 2 draws.
Using systematic listing we get,
WWW, WWD, WDW, DWW, WWL, WLW, LWW, DDW, DWD, WDD.
6. A coin is flipped three times and the result is recorded. Make a list of the possible outcomes.




There are 8 possible outcomes if the order of the combinations matters. A single coin is being flipped three times so this suggests the order will matter.
Systematic listing strategies GCSE questions
1. A coin is flipped and a 5 sided spinner labelled 1 to 5 is spun.
List the possible outcomes. The first one is done for you.
H1,
(2 marks)
All combinations with H included.
(1)
Complete list (H1), H2, H3, H4, H5, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5 .
(1)
2. A football team has four games remaining of the season and needs to achieve at least 8 points to avoid relegation.
A win gives 3 points, a draw gives 1 point, and a loss gives 0 points.
Using W for a win, D for a draw and L for a loss, list the possible combinations that will help the football team achieve at least 8 points.
(3 marks)
A systematic approach to listing seen.
(1)
At least 10 combinations, which include some with L.
(1)
All 15 combination listed.
(1)
\begin{aligned} &WWWW, WWWD, WWDW, WDWW, DWWW, WWWL, WWLW, WLWW, LWWW, \\\\ &WWDD, WDWD, WDDW, DDWW, DWDW, DWWD \end{aligned} .
3. A free meal for kids at a cafe offers a choice of sandwich, drink and fruit.
| Sandwich | Drink | Fruit |
| Cheese (C) Ham (H) Egg (E) |
Water (W) Smoothie (S) |
Banana (B) Apple (A) |
List all of the possible meal combinations.
(3 marks)
Systematic approach seen.
(1)
All combinations with one sandwich seen.
(1)
All 12 combination given.
(1)
CWB, CWA, CSB, CSA, HWB, HWA, HSB, HSA, EWB, EWA, ESB, ESA.
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Apply systematic listing strategies, including use of the product rule for counting
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.